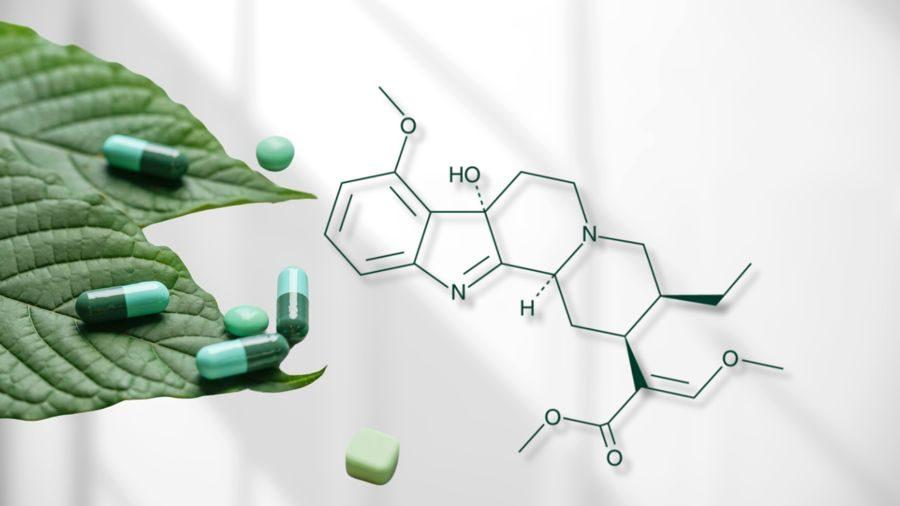
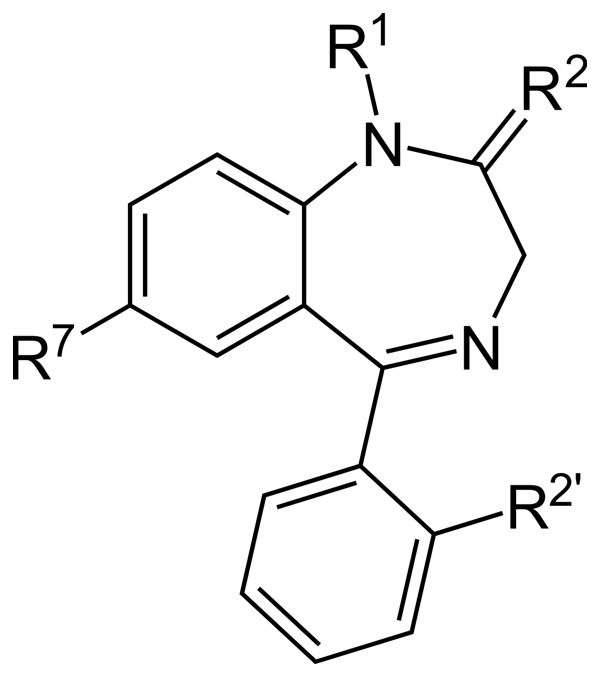
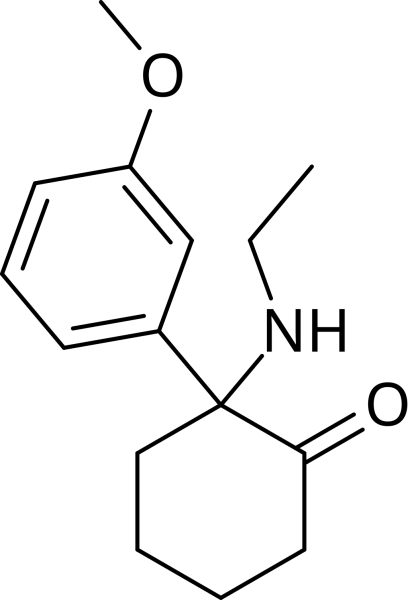
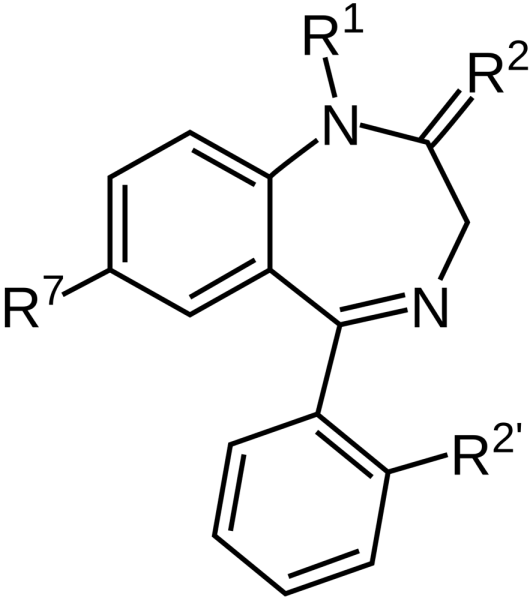
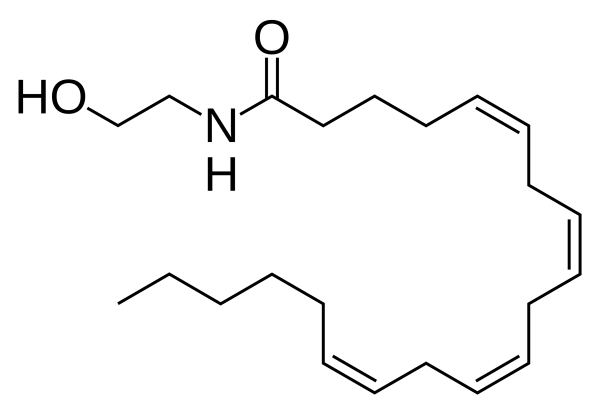
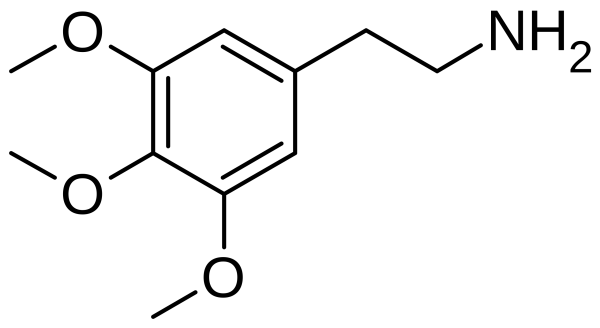
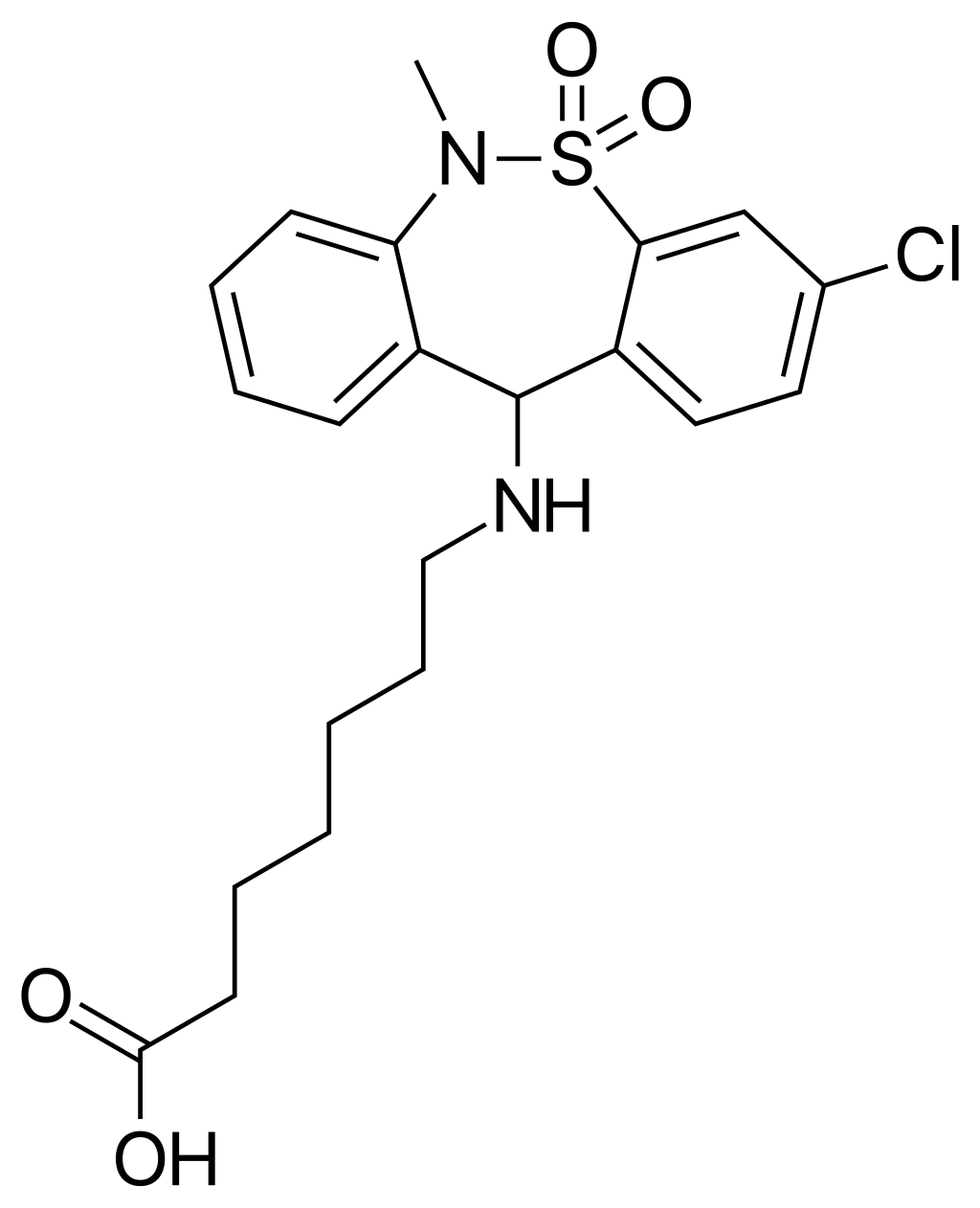
Mitragynine
Kratom has gained popularity as a legal remedy, a “natural” and readily available alternative to prescription analgesics and synthetic psychoactive substances. It was originally used in Asian countries, but globalization has helped spread this semi-legal “semi-medicine” to the West. Kratom has a specific feature: in small doses it acts as a stimulant, but in largeRead More