Overview of synthetic and design dissociatives
Ketamine is the main substance, the design of analogues was taken from it. We have a separate article about K and trip reports once and twice.
Ketamine hydrochloride (“Ketamine”) is widely used for medical purposes all over the world. This drug is widely used in veterinary practice, during various types of surgical interventions.
The ability of the drug to cause hallucinations with mystical experiences is associated with the function of central agonism against 5-HT2A receptors, antagonism against NMDA receptors, and high affinity for mu/delta/sigma opioid receptors.
With non–medical use, ketamine is usually consumed by inhaling powder, smoking, or rectal administration, in wide dosage ranges – from 25 to 300 mg.
Psychotropic effects produced on the body include a violation of the pace of thinking, a feeling of “bifurcation of one’s self”, depersonalization disorders, violation of the body schema, confusion of consciousness before depersonalization. And the so-called k-hole. A place where space-time ceases to exist.
With prolonged use, there may be an increase in tolerance, the formation of mental dependence, the formation of “chronic flashbacks”, the development of symptoms of the schizophrenic spectrum, chronic perception disorders, illusory disorders that may persist in the state, even after cessation of use.
A third of recreational Ketamine users have various urological problems: neurogenic bladder, urinary incontinence, pain in the suprapubic region, blood entering the urinary tract, decreased bladder capacity, changes in bladder tissues. Of the other somatic problems directly related to the use of Ketamine, various disorders of the gastrointestinal tract can be noted.
The use of high doses when consumed may be the cause of the development of cardiovascular and respiratory failure. Paresthesia, muscle hypotension, various perception disorders-due to use, can cause injuries, burns, falls.
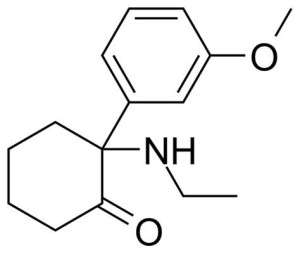
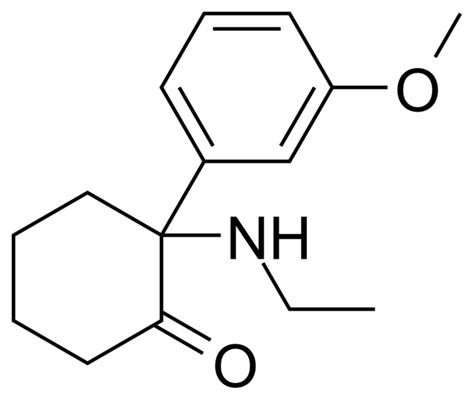
There is a separate article about MXE and trip reports.
MXE, “Special M” is a designer analogue of Ketamine that has appeared relatively recently on the shadow market.
It is consumed orally (by mouth), by inhaling the powder, sublingual reception is possible. The dose range is from 5 to 100mg.
“MXE” has antagonism against NMDA receptors, and also acts as an inhibitor of dopamine and serotonin transport.
Most of the “MXE” consumers indicate in self-reports about prolonged psychotropic effects after use.
Shadow manufacturers position this cat as an absolutely safe analogue of Ketamine. However, a closer study and observation of patients using “Special M” causes serious concern among specialist doctors.
In a state of acute intoxication, cases of severe cerebellar disorders, epileptiform disorders have been described. Several fatal cases have been described after the use of “MXE”.
Are new designer drugs. Read more about MXP in our FAQ.
They act as NMDA receptor antagonists, act as serotonin transport inhibitors, dopamine agonists, and opioid agonists.
These substances are consumed orally, by inhalation of powder, intravenous administration – in dosages from 50 to 150 mg. The duration of action is from 8 to 12 hours.
When using high doses of “DND” and “MXP”, over 180 mg., serotonin syndrome may develop.
“DXM” is an over-the-counter drug for the treatment of cough in a number of European and American countries. It acts as an antagonist against NMDA receptors, and a very weak agonist against mu-opioid receptors, can inhibit serotonin transport.
About DXM we have separate articles FAQ 1 & FAQ 2, FAQ 3, trip reports and more. Comparison of LSD and DHM.
Many authors point to the possibility of increasing tolerance, and the formation of phenomena of mental and physical dependence, with recreational use of the drug.
After prolonged abuse of Dextromethorphanan during its deprivation, various kinds of mental disorders develop: mania, anxiety disorders, dysphoric reactions, persistent insomnia, flashbacks.
Abrupt cessation of use also causes a number of somatic withdrawal symptoms: vomiting, diarrhea, pain in various muscle groups, intense sweating.
The use of high doses of Dextromethorphan for non-medical purposes may cause the development of serotonin syndrome.
There is also a known side effect of DHM, such as Olney’s Lesion, which consists in organic brain lesions.
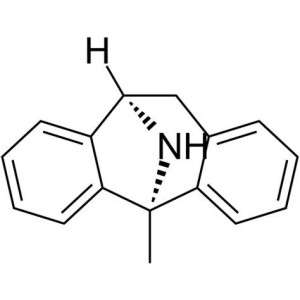
Disocylpin (INN), also known as MK-801, is a non-competitive antagonist of the NMDA receptor, a glutamate receptor discovered by the Merck team in 1982.
Disocylpin blocks NMDA receptors depending on usage and voltage, since the channel must open to bind the drug inside it.
The drug acts as a strong anticonvulsant and has the dissociative properties of an anesthetic, but it is not used clinically for this purpose due to brain lesions, called Olney lesions, in the tested rats.
Disocilpin is also associated with a number of negative side effects, including cognitive impairment and psychotic spectrum reactions.
Although ketamine can also cause temporary psychosis in some people, its short half-life and lower efficacy make it a safer clinical option. However, disocilpin is the most commonly used non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist in animal models to simulate psychosis for experimental purposes.
It has been found that dizocilpin acts as an antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It is known that it binds to serotonin and dopamine inhibitors, inhibiting them.
Disocylpin has great potential for use in research on the creation of animal models of schizophrenia. It has been shown that not only temporary use simulates psychosis, but also chronic administration in laboratory animals leads to similar neuropathological changes as in schizophrenia.
Dizocilpin is used as a recreational minkotek. In this context, little is known about its effects, dosage and risks. The high efficacy of dizocilpin makes it difficult to accurately dose compared to other similar drugs.
As a result, the chances of overdose are high. Users say that it is not as pleasant as other dissociative drugs, and is often accompanied by strong auditory hallucinations. In addition, disocylpine is much longer lasting than similar dissociative drugs such as ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP), and causes much stronger amnesia and residual thinking problems, which prevents its adoption as a recreational drug.
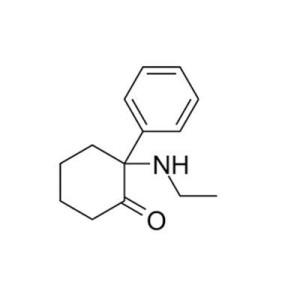
DXE, DCK, 2′-Oxo-PCM is a dissociative anesthetic that is sold online as a designer drug. It has also been proposed for the treatment of bacterial, fungal, viral or protozoal infections and for immunomodulation in doses of 2 mg per day.
It is used in a dosage of 5-40 mg, the duration of action is 30-90 minutes when smoking. When eating 10-50mg, the duration is 4-6 hours.
An alkaloid found in several different plant species of the Papaveraceae family, such as Glaucium flavum, Glaucium oxylobum and Corydalis yanhusuo, and other plants such as Croton lechleri in the Euphorbiaceae family.
It has broncholytic properties and anti-inflammatory effects, is used as an antitussive agent in some countries.
Glausin can cause side effects such as sedation, fatigue and a hallucinogenic effect characterized by colorful visual images and has been found to be marketed as a new psychoactive drug.
Recently, reports have been published about the recreational use of glaucine, and the effects include dissociative type symptoms; a feeling of loneliness “in another world”, as well as nausea, vomiting and dilated pupils.
There are also obvious dissociative symptoms, as well as lethargy, fatigue and hallucinations. The study of side effects in clinical settings also reports that hallucinatory effects manifest themselves as vivid and colorful visualizations. Patients also report that they clearly see the world around them, but feel “disconnected” from it.
Oral dosages are 10-40 mg, the effect is 4-6 hours.
NEDPA and EPE is a dissociative anesthetic that is sold online as a designer norcotec. It is illegal in some countries as a structural isomer of the banned opioid drug lefetamine, but it is sold in countries where it is not yet banned.
In Sweden, efenidine is going to be considered as an analogue of the banned substance lefetamine.
In Canada, MT-45 and its analogues have been identified as Schedule I controlled substances. Possession without legal authority can lead to imprisonment for up to 7 years.
